
Our design process combined our first-hand experiences learning to weave smart textiles with the development of a design tool for smart textiles. We describe our software and its novel features, present examples of smart textiles that can be created using these weaving techniques and practices, and reflect upon feedback from interviews with five practitioners in the smart textiles field.
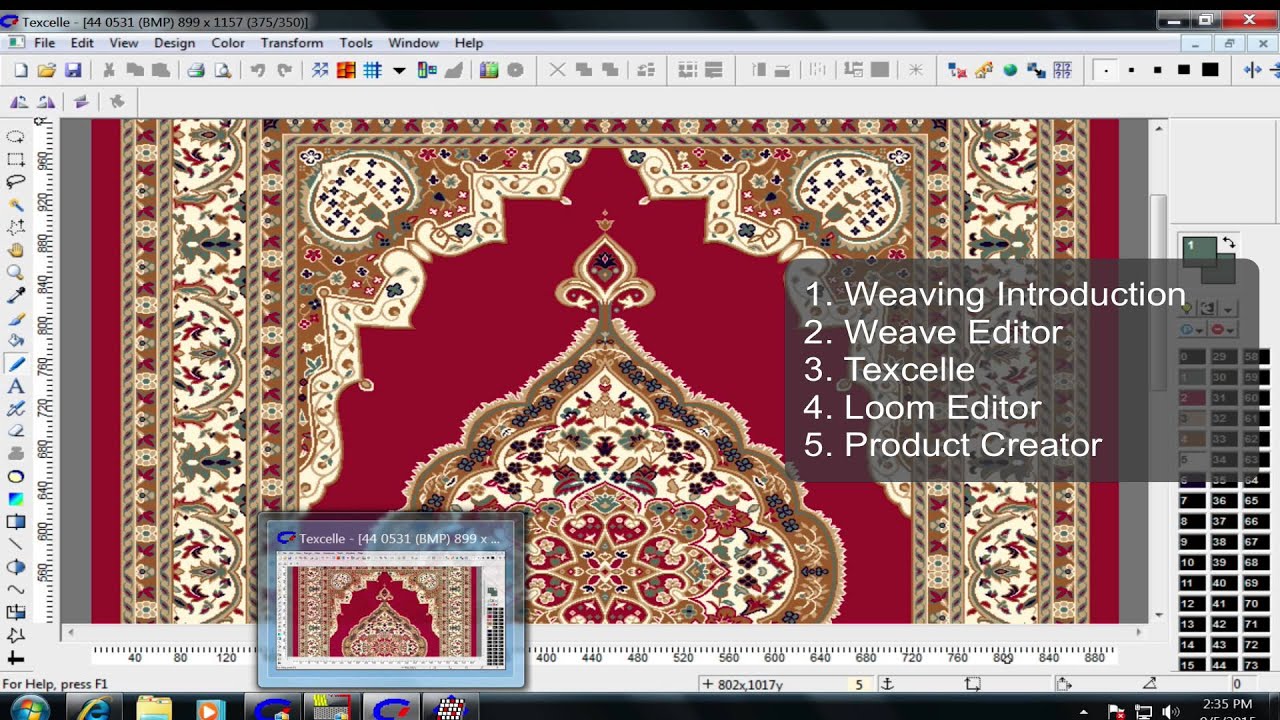
In departure from existing weaving tools, AdaCAD offers specific features to help overcome the unique challenges that come with designing woven circuitry, such as understanding yarn connectivity and built-in support for common smart textiles techniques. This paper presents AdaCAD, a web-application we developed to support designing woven structures and circuits in tandem. As Posch and Fitzpatrick argue, ”Using existing tools from either domain thus inherently ignores essential aspects of electronic textile making processes” . AdaCAD allowed us to view the design as yarn paths (d) or traditional weaving drafts (e).Īs this domain grows, there is a need for new tools that foster community between multiple fields of expertise and are accessible to a range of skill levels (for circuit designers and/or weavers). We used the tool to create a prototype we developed with multiple regions of touch sensing and color change (a, b, c).

Figure 1: AdaCAD supports the design of woven smart textiles by augmenting traditional weaving drafts with smart textiles specific operations and views.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
